RESEARCH:
WP2: Better understanding of age-related gait and balance impairments
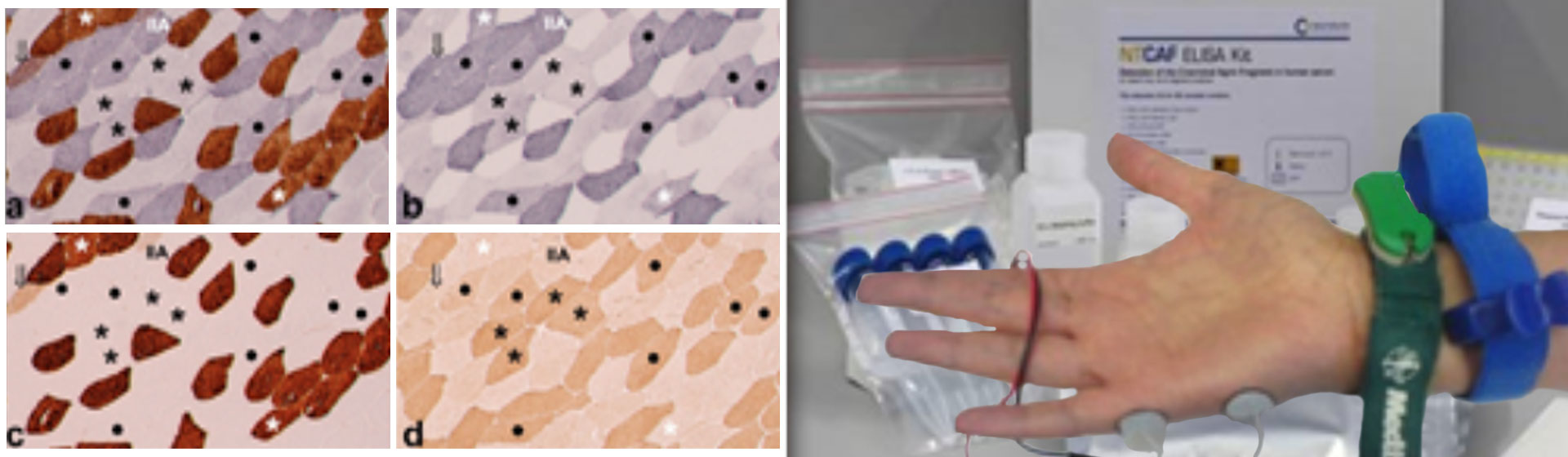
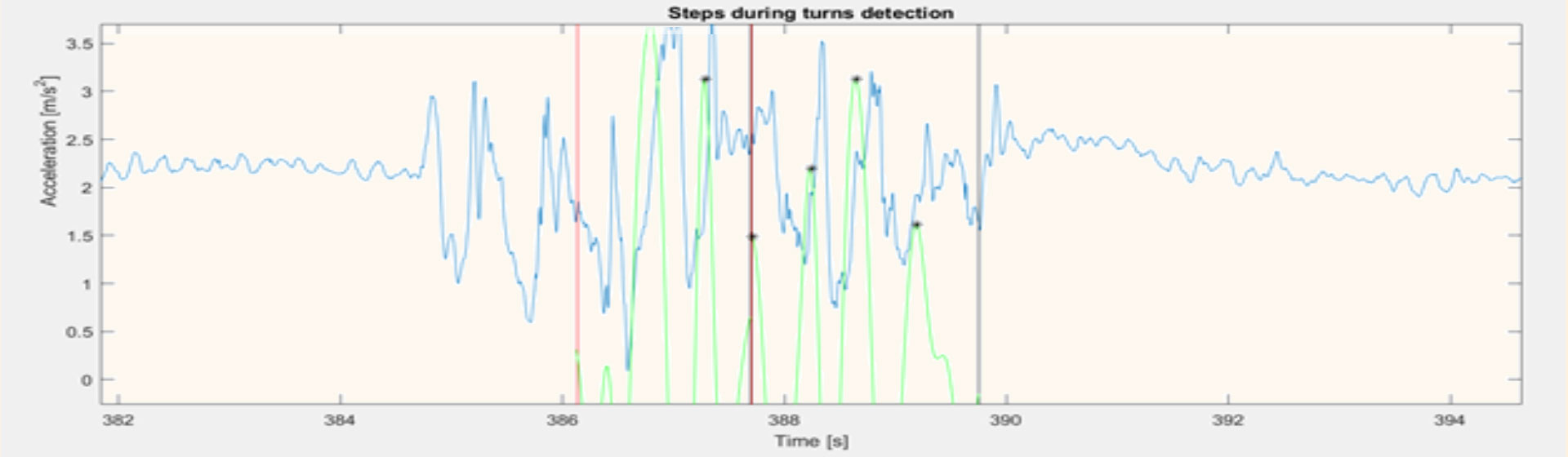
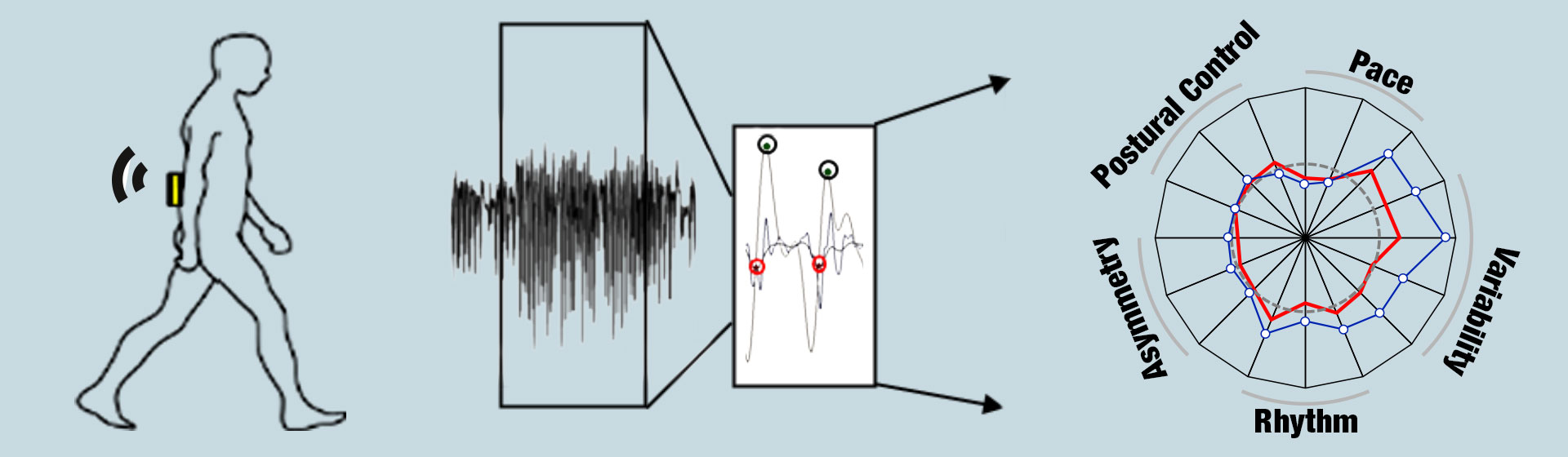
WP2 aims to provide a fundamental understanding of gait and balance deficits in older adults. Cohorts span from older individuals with relatively preserved gait and balance functions, over frail patients with sarcopenia (i.e., with degenerative loss of skeletal muscle mass and function) to three relevant stages of Parkinsonism: prodromal, early clinical and advanced clinical stages. Assessment strategies range from high-end perturbation platforms in the lab to body-worn sensor-based assessment in the home environment, and include histological and body fluid investigations.
WP3: Specific treatments of age-related gait and balance deficits, and falling
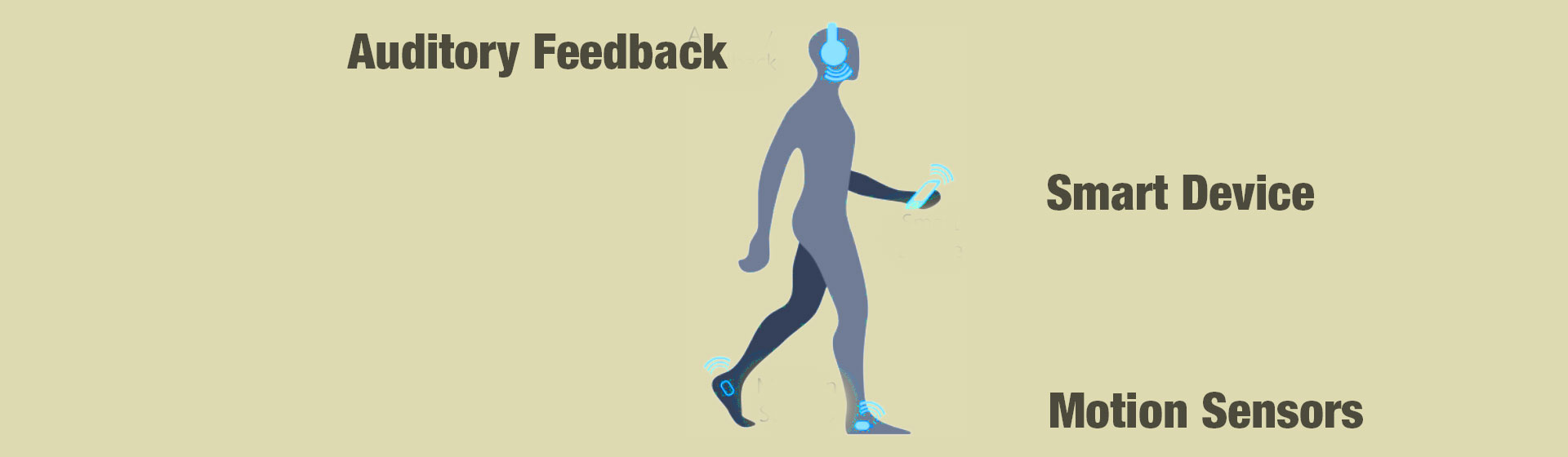
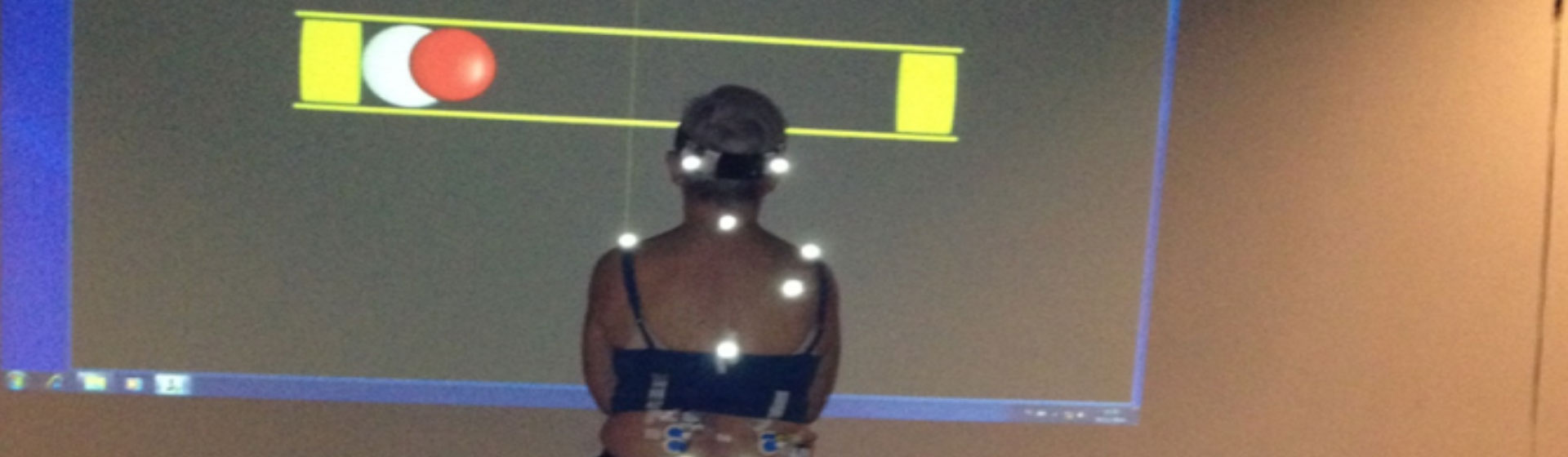
WP3 aims to develop new and specific training paradigms for gait and balance deficits in older adults who are at risk for falling, or have already fallen. Assessment approaches range from sophisticated standing and walking balance training approaches, over real-time acoustic feedback balance training to a drug trial investigating the influence on attention during gait initiation. The knowledge generated by these proof-of-principle studies will inform the development of new approaches to rehabilitation for the ageing population.
WP4: Harmonisation of assessments across the network, active involvement of study participants, meta-analysis of obtained data
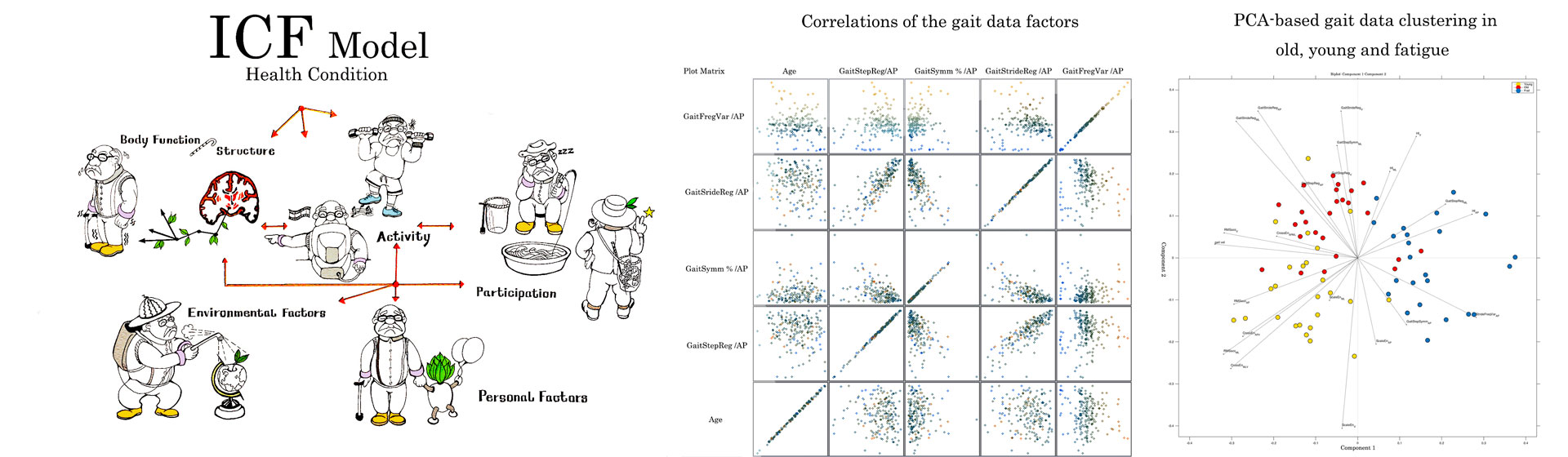
WP4 will increase integration and sustainability of Keep Control by three actions: Harmonisation of assessments across the network based on the ICF model, meta-analysis of all data obtained within the proposed ETN, and active involvement of study participants through the inclusion of a web-based digital medical record.